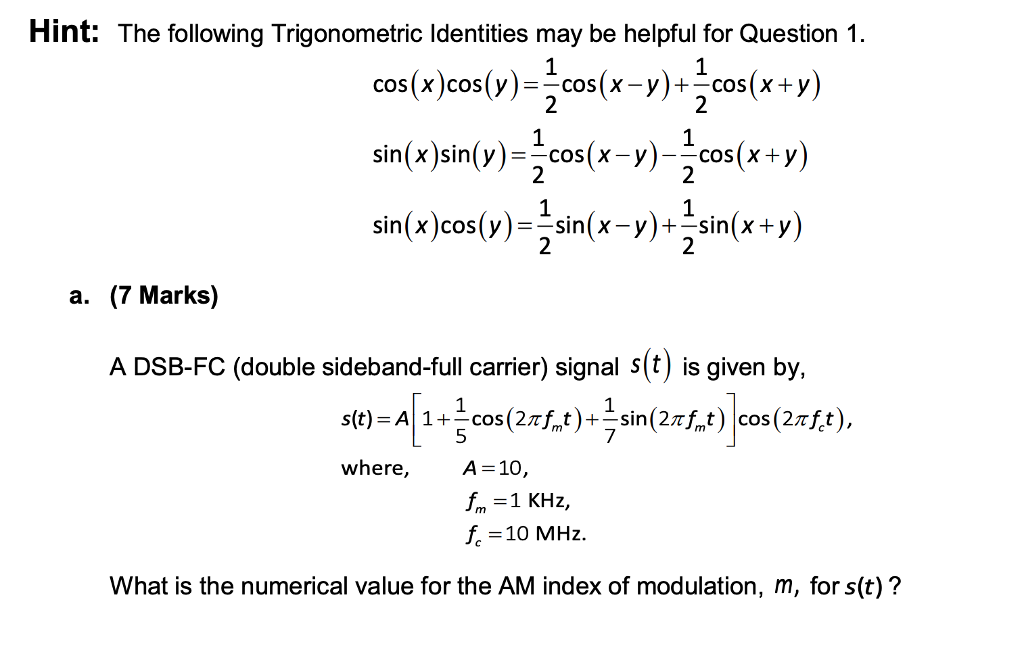
Solved Hint The following Trigonometric Identities may be
Solution Given, sin2y+cos xy =k Differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get d dx(sin2y+cos xy =k) = d dx(k) ⇒ d dx(sin2y)+ d dx(cos xy)= 0 2sin y cos ydy dx+(−sin xy) d dx(xy) =0 (U sing product rule d dx(f(g(x))) =f (x) d dxg(x)) ⇒ sin 2ydy dx−sin xy(xdy dx+y.1) =0 (∵ sin 2x= 2sin x.cos x)

[最新] y'=sin(x y) cos(x y) 508659(xdyydx)y sin(y/x)=(ydx+xdy)x cos(y/x)
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with step-by-step solutions. Our math solver supports basic math, pre-algebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more.

Sin X Cos Y Identity patofia
Free math problem solver answers your trigonometry homework questions with step-by-step explanations.
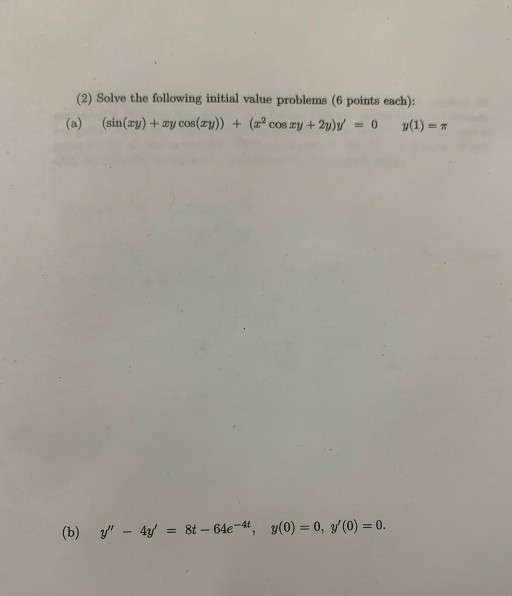
Solved (2) Solve the following initial value problems (6
Best answer We are given with an equation sin2y + cos (xy) = k, we have to find [Math Processing Error] d y d x at x = 1, y = [Math Processing Error] π 4 by using the given equation, so by differentiating the equation on both sides with respect to x, we get,

Solved Consider the vector field F(x, y, z) = y cos (xy) i +
Join Teachoo Black. Ex 5.3, 7 Find 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 in, sin2 𝑦 +cos 𝑥𝑦 =𝜋 sin2 𝑦 +cos 𝑥𝑦 =𝜋 Differentiating both sides 𝑤.𝑟.𝑡.𝑥 . (𝑑 (sin2 𝑦 + cos 𝑥𝑦))/𝑑𝑥 = (𝑑 (𝜋))/𝑑𝑥 (𝑑 (sin2 𝑦))/𝑑𝑥 + (𝑑 (cos〖 𝑥〗 𝑦))/𝑑𝑥= 0 Calculating Derivative of.

Calculus Archive April 23, 2017
Trigonometric identities are equalities involving trigonometric functions. An example of a trigonometric identity is. \ [\sin^2 \theta + \cos^2 \theta = 1.\] In order to prove trigonometric identities, we generally use other known identities such as Pythagorean identities. Prove that \ ( (1 - \sin x) (1 +\csc x) =\cos x \cot x.\)

Q.1 (2xy sin x)dx + (x cos y)dy= 0. q.2 (1+ 2x/ y2) dx 2y x2 y2dy = 0. q.3
Solution Verified by Toppr We have, sin2y+cosxy = k Differentiating both sides with respect to x, we obtain ⇒ d dx(sin2y)+ d dx(cosxy) = d(π) dx = 0. (1) Using chain rule, we obtain d dx(sin2y)= 2siny d dx(siny) = 2sinycosydy dx.. (2) and d dx(cosxy) =−sinxy d dx(xy) = −sinxy[y d dx(x)+xdy dx]
What is the general solution of this differential equation (𝑟 + sin 𝜃 − cos 𝜃) 𝑑𝑟 + 𝑟 (sin 𝜃
Solve Solve for k k = cos(xy) + (sin(y))2 Quiz Trigonometry sin2y +cosxy = k Videos 03:27 Evaluar expresiones con dos variables: fracciones y decimales Khan Academy 06:27 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring 1 Khan Academy Evaluar expresiones con variables: problemas verbales (artículo) | Khan Academy khanacademy.org 05:38

Q25 If cos(xy)=k, where is a constant & xy≠nπ, n∈z, then dy/dx is YouTube
`sin^(2)y + cos xy = k` Differentiate both sides w.r.t. x ` 2sin y cos y (dy)/(dx) + (-sin xy) (d)/(dx)(xy) =0` `rArr sin 2y (dy)/(dx)-sin xy(x(dy)/(dx)+ y .1)=0`

cos(x+y).cos(xy)=cos^2ysin^2x Brainly.in
Exercise : Find the gradient of. Answer. The directional derivative can also be generalized to functions of three variables. To determine a direction in three dimensions, a vector with three components is needed. This vector is a unit vector, and the components of the unit vector are called directional cosines.

`sin^(2)y + cos xy = k` YouTube
cos(x+y) = cos\\ x* cos\\ y - sin\\ x* sin\\ y cos(x-y) = cos\\ x*cos\\ y + sin \\ x*sin\\ y sin^2 x +cos^2\\ x= 1 cos(x+y) = cos\\ x* cos\\ y - sin\\ x* sin\\ y cos.

Differentiate sin^2y + cos xy = K
Learn Find Dy Dx Sin2y Cos X Y from a handpicked tutor in LIVE 1-to-1 classes Get Started Find dy/dx: sin 2 y + cos xy = κ Solution: A derivative helps us to know the changing relationship between two variables. Consider the independent variable 'x' and the dependent variable 'y'.
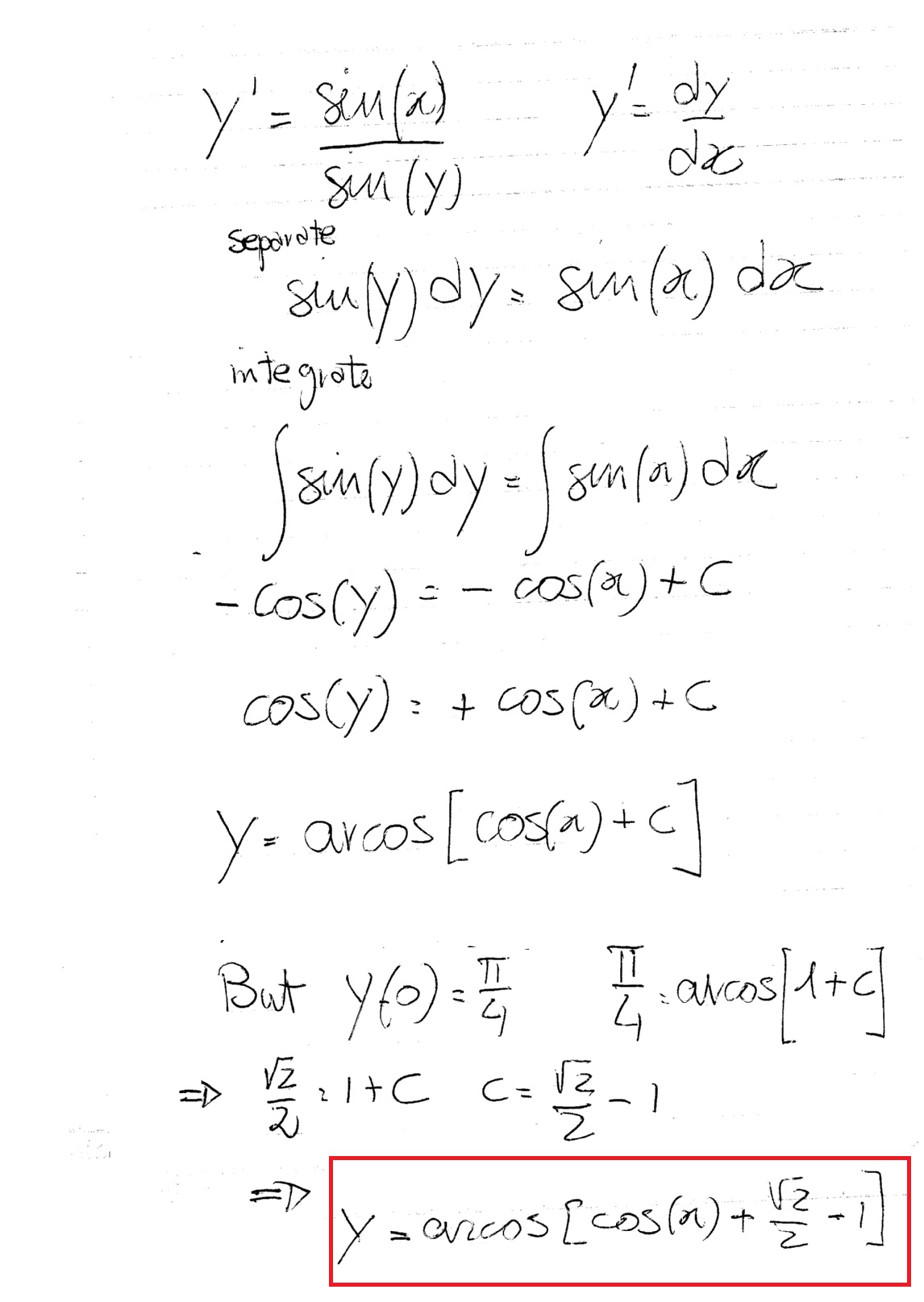
π/2sin^1x 278834π/2sin^1x Saesipjos5r8y
In this video we will discuss some question from chapter - 5 of ncert exemplar problems with more than one methods and also some short or useful methods for.

If sin(xy) + cos(xy) = 0 then dy/dx equals Q 39 JEE MAINS YouTube
The following (particularly the first of the three below) are called "Pythagorean" identities. sin 2 ( t) + cos 2 ( t) = 1. tan 2 ( t) + 1 = sec 2 ( t) 1 + cot 2 ( t) = csc 2 ( t) Advertisement. Note that the three identities above all involve squaring and the number 1. You can see the Pythagorean-Thereom relationship clearly if you consider.
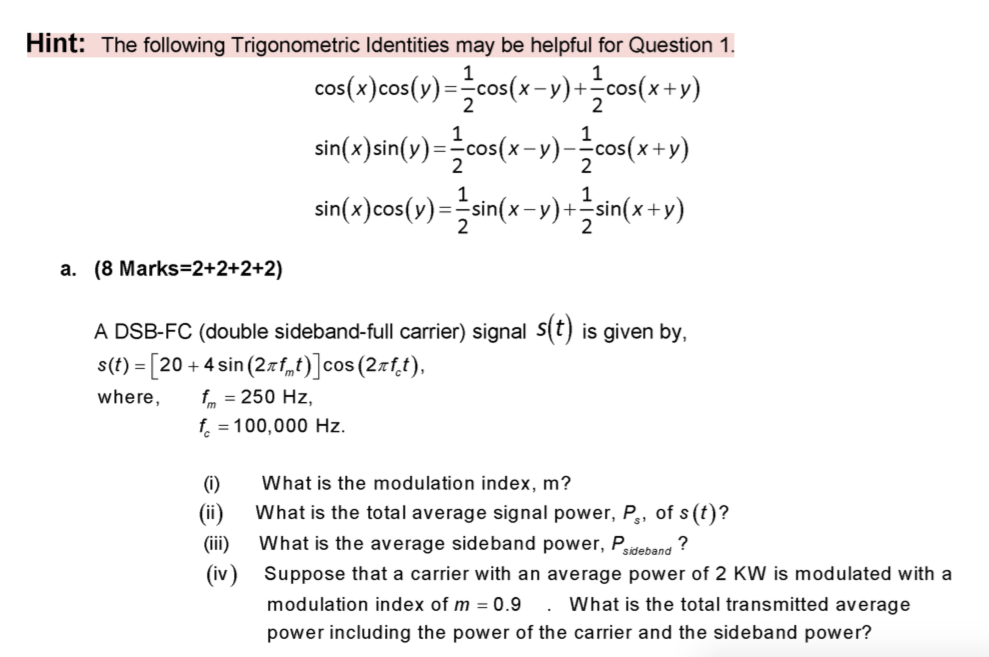
[最新] y'=sin(x y) cos(x y) 508659(xdyydx)y sin(y/x)=(ydx+xdy)x cos(y/x)
Solution Verified by Toppr sin2y+cosxy =k 2sinycosydy dx+(−sinxy)(y+xdy dx)= 0 Put y = π 4,x = 1 2× 1 √2× 1 √2dy dx− 1 √2(π 4+ dy dx) = 0 dy dx− 1 √2 dy dx = π 4√2 dy dx = π 4(√2−1) Was this answer helpful? 0 Similar Questions Q 1 If y =(2−3cosx sinx), find dy dx at x = π 4 View Solution Q 2 Find dy dx in the following questions: sin2y+cos xy = k
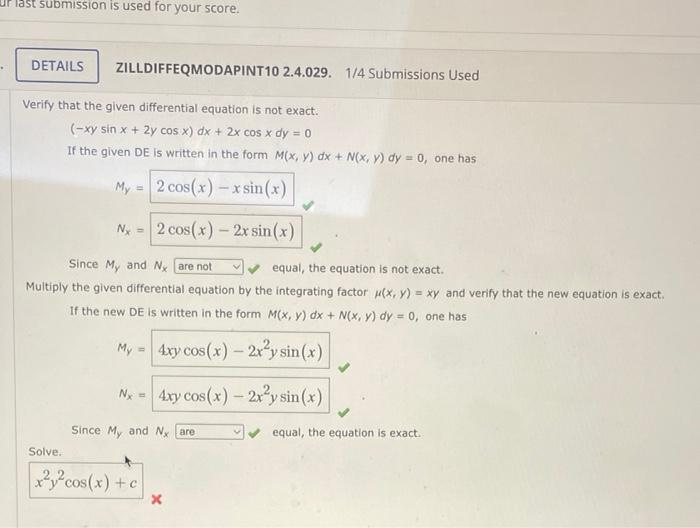
Solved Verify that the given differential equation is not
sin^2y+cos xy=k, find dy/dx.|CLASS 12|CBSE|MATHS|BOARDS|IMP TOPIC